| July 27, 2022 |
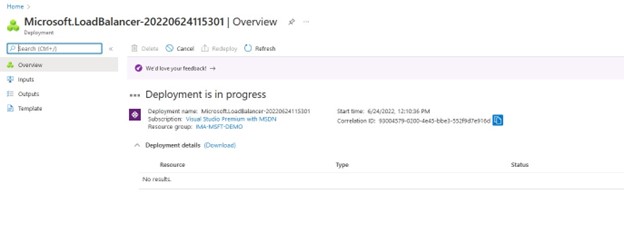
Introducing the Generic Load-Balancer Kit for SIOS LifeKeeper and Microsoft Azure |
||||||
| July 24, 2022 |
Solution Brief: High Availability for SAP S4/HANA |
||||||
| July 17, 2022 |
Fact Sheet: BMS High Availability |
SIOS DataKeeperAdd SIOS DataKeeper to a Windows Server Failover Clustering environment to create a SANless cluster where traditional shared storage clusters are impossible or impractical, such as cloud and hybrid cloud environments. Fast, efficient host-based replication synchronizes local storage on all cluster nodes for maximum configuration flexibility. Or, add replication to your existing SAN-based Windows cluster for DR.
|
SIOS Protection SuiteSIOS Protection Suite for Linux lets you run your business-critical EHR applications on-premises or in a flexible, scalable cloud environment, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure without sacrificing performance or HA/DR protection. SIOS clusters uniquely failover across cloud regions or availability zones for true HA protection.
|
HA/DR for Building Management Systems
Fact Sheet
BMS Systems Protected
|
Environments & Platforms Protected
|
Databases and ERPs ProtectedSQL Server, SAP, SAP S/4HANA, Oracle, SharePoint Learn More
|
Healthcare Case StudiesChris O’Brien Lifehouse Cancer Treatment Center, Allyn Hospital, Carroll Hospital, Leading Healthcare Provider. Learn More |
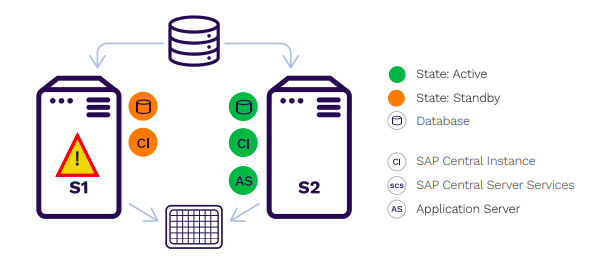
configuration, enabling failover clusters in physical, virtual, cloud, and hybrid cloud environments.
- Get a free trial of SIOS High Availability and Disaster Recovery Clustering Software
- Learn more about SIOS DataKeeper
- Download Fact Sheet PDF
Reproduced with permission from SIOS
SIOS LifeKeeper – High Availability for Linux
SIOS LifeKeeper – High Availability for Linux
Enterprises running business-critical applications such as SAP, S/4 HANA, SQL Server, MaxDB and Oracle face a dilemma. Even brief periods of downtime for these complex workloads could have catastrophic consequences. But traditional HA clustering can be complex and costly. Moving to the cloud isn’t the answer as cloud availability SLAs only cover hardware. They can’t provide HA and DR for stateful applications without degrading performance in the cloud. Shared storage used in traditional on-premises clustering is not an option in some clouds and is too complex and costly in others to be practical. Many HA clustering solutions cannot fail over cloud regions and availability zones – limiting the level of disaster recovery they can provide. Open Source clustering isn’t the answer. It requires complex scripting and is prone to human error and failure. The manual steps required to ensure complex ERPs or databases failover can leave correctly. IT teams are hesitant to perform regular maintenance and failover testing.
SIOS has the Solution.
SIOS LifeKeeper delivers high availability and disaster recovery that ensures systems, databases, and applications operate when and as needed.
- Unique, application-aware recovery kits make creating and managing high availability clusters in complex environments such as SAP, S/4 HANA, SQL Server, MaxDB and Oracle straightforward and error-free.
- Complete monitoring, unlike HA solutions that only monitor server operation, SIOS LifeKeeper monitors the application stack network, storage, OS, and application.
- Advanced, application-aware technology automates configuration and validates inputs – enabling accurate configuration five times faster than open-source clustering software and ensuring failovers are reliable and maintaining application best practices.
In the cloud, SIOS clusters fail across regions and Availability Zones for maximum DR protection. For customers who want to deploy multiple clusters, SIOS LIfeKeeper’s cloning feature allows you to create multiple identical clusters using consistent, predefined settings and integrated best practices. SIOS LIfeKeeper comes in a bundle called the SIOS Protection Suite that includes application-specific recovery kits and efficient replication for SANless clustering and DR. Get 99.99% availability and disaster protection for critical Windows or Linux workloads running on-premises, in the cloud, or hybrid cloud environments. Schedule a demo or sign up for your free trial today.
Reproduced with permission from SIOS
High Availability Lessons from Disney and Pixar’s Soul
High Availability Lessons from Disney and Pixar’s Soul
In Disney and Pixar’s Soul, the main character Joe Gardner (voiced by Jamie Foxx) has dreamed of being a professional jazz pianist. However, despite his many attempts, to his mother’s dismay, he finds himself miles away from his dream, living as “a middle-aged middle school band teacher.” But then, “thanks to a last-minute opportunity to play in jazz legend Dorothea Williams’ quartet, his dreams seem like they are finally about to become a reality. That is until “a fateful misstep sends him to The Great Before—a place where souls get their interests, personalities, and quirks— and Joe is forced to work with a “22”, an ancient soul with no interest in living on earth, to “somehow return to Earth before it’s too late (D23.com).”
Disney and Pixar’s Soul is a great movie with lots of interesting and relatable characters, humorous, descriptive and sometimes disturbingly relatable takes on life, purpose and living. But, it is also a movie with rich leadership lessons, life lessons, and lessons on higher availability.
Seven thoughts on Higher availability from Disney and Pixar’s Soul.
1. Pay attention to what’s going on
In Disney and Pixar’s Soul Joe lands his dream gig. But as Joe starts walking and sharing the great news, he is so engaged with his phone that he walks into the street, nearly gets crushed under a ton of bricks, and then he wanders dangerously towards an open, but clearly marked manhole. So what’s the lesson for higher availability– pay attention. Pay attention to the alerts and error messages from your monitoring and recovery solutions. Pay attention to the changes being made by your hosting providers, and especially to critical notices from vendors and partners and security teams. Alerts and warnings are there for a reason, failing to address them or take the appropriate action when you see the warning could lead you into a deep hole.
2. Don’t fall into a hole
Oblivious to the warnings, or ignoring them, Joe finally meets his end when he falls into an open manhole and becomes a soul. This immediately alters his dreams and plans. So, what hole could your enterprise be poised to fall into? Are there open holes lurking in the path of your enterprise such as: coverage holes, versioning gaps, holes in maintenance plans and reality, or even a black hole with vendor responsiveness? Look around your environment, what holes could you fall into beyond the obvious single points of failure? Is there a warning that you have an open hole related to unprotected critical applications, communication gaps between your teams, or even holes in your process and crisis management. Don’t fall into a hole that could damage or even end your high availability.
3. Don’t rush high availability
After becoming a soul Joe begins actively trying to get back to his own body. When he gets paired with 22, she takes him to Moonwind who agrees to try to help him find his body, which they do. But Joe becomes too eager to jump back into his body, despite Moonwind’s caution. In his rush both he and 22 fall back to earth, but Joe ends up in the body of a cat and 22 ends up in his body. Like Joe if we aren’t patient, the jump happens too soon and we end up in a precarious or even worse situation. We may not be in the body of a cat, but we may also be far from the best position necessary to maintain HA. Jumping too soon looks like:
- Deploying software without an architecture or holistic solution
- Deploying in production without testing in QA
- Deploying into the cloud without understanding the cloud or what the cloud means by HA
- Deploying into production based on a timeline and not completed acceptance tests
- Deploying without a purpose built, commercial grade solution for application monitoring and orchestration
4. Don’t quit too soon – high availability is never easy
When Connie, a young trombone player, comes to the apartment of her teacher she is frustrated and wants to quit. She begins by telling Joe (who is actually 22 in Joe’s body) that she’s frustrated and that she just wants to give up and quit. But after a few moments, she plays one last piece on the trombone and realizes that it is too soon to quit. In higher availability, we are all a lot like Connie. Sometimes, a difficulty makes us feel like we are at the end of our rope and want to quit. Sometimes an outage will make us feel certain that it’s time to throw in the towel. Don’t be so quick to quit. HA is never easy, never! But, it is always too soon to quit striving to end downtime, so like Connie, maybe we just need to keep at it. Which leads me to the next lesson.
5. You haven’t tried everything
In the movie 22 is a soul who hasn’t lived yet. She believes that she has tried all the possible things to give her a spark, but when she falls into Joe’s body she realizes there is a lot that she hasn’t tried. In creating a higher availability solution, it can be easy to feel like you’ve tried everything and every product, but most likely you haven’t. A fresh perspective, or looking at the challenges and problems with a new set of eyes may help you improve your system and enterprise availability.
Some things to try for higher availability can be simple, such as:
- Set up additional alerts for key monitoring metrics
- Add analytics.
- Perform regular maintenance (patches, updates, security fixes)
- Document your processes
- Document your operational playbook
- Improve your lines of communication
- Perform regular maintenance
Other ideas may require more work, research, time and money but could be worth it if you haven’t explored them in the past.
Ways to improve your higher availability with more time and effort include:
- Remove hacks and workarounds.
- Create solid repeatable solution architectures
- Go commercial and purpose built
- Hire a consultant
- Audit and document your architecture
- Upsize your VM; CPU, memory, and IOPs
- Add additional redundancy at the zone or region level
6. Ask more (and better) questions
After Joe, as Mr. Mittens, accidentally cuts a path down the middle of his hair, Mr. Mittens and Joe have to take a trip to see Dez, Joe’s barber. While Joe is in the barbers chair with Dez they begin having a conversation about purpose, life, existential existence and more. After the haircut, 22 asks Dez why they never had conversations like this before, about Dez’s life. Dez responds that he’d never asked before. Sometimes we can get so tunnel focused in solutions, in methods for the cloud or on-premise, in languages and architectures, and in telling others what we are doing that we forget to ask questions that can open up a whole new world. As Joe asked questions he learned more about Dez, and about himself. Perhaps the lesson for better HA is to start asking more questions about our solution, about the architecture, about the business goals and challenges, about the end customer goals, about our teams, and even about our roles and responsibilities within the bigger picture.
Some simple questions to increase our availability include:
- If a disaster happens tomorrow, what system, process, product, or solution would be the cause?
- What is the single most important thing to protect? Application, data, metadata, all of the above?
- What RPO can our applications and databases tolerate?
- What won’t our customers tolerate?
- What am I missing?
- Where do we have this architecture documented?
- What don’t I understand?
7. Perseverance pays off
“The counts off,” says Terry. Tasked with keeping track of the entrants to The Great Beyond, Terry is meticulously counting the number of souls that should be arriving or have arrived. After Joe takes a detour to The Great Before, Terry grows determined to find the missing soul and fix the tally. When he begins his work, he is in a long corridor of file cabinets that stretch as far and as high as the eye can see. But after a while, he finds the file of Joe and discovers that Joe has found a loophole and that is why the count was off. The same perseverance displayed by Terry will also pay off in the realm of higher availability. In the face of a daunting uncertainty, a plethora of log files, and an ocean of possible failure scenarios the moments of perseverance to uncover and then remedy problems before they occur, or analyze and remediate them effectively after they occur will lead us to the better outcomes we desire. Similarly, a lack of diligence and perseverance will mean that the same problem will likely resurface later, even in a new environment with new software.
As the movie Soul ends, Joe returns to the Great Before, finds and then convinces 22 to take her Earth pass and take the plunge. Reminiscent of when she fell to earth with Joe, she takes another plunge. To the dismay of my children, the movie ends without describing what 22 makes of her life or the new opportunities that follow. She simply leaps from the Great Before with an anticipation of what will happen next. Perhaps we too stand at a moment where we can take the plunge… a moment in the “Great Before” and an opportunity to make this a year of additional higher availability.
– Cassius Rhue, VP Customer Experience
Reproduced with permission from SIOS

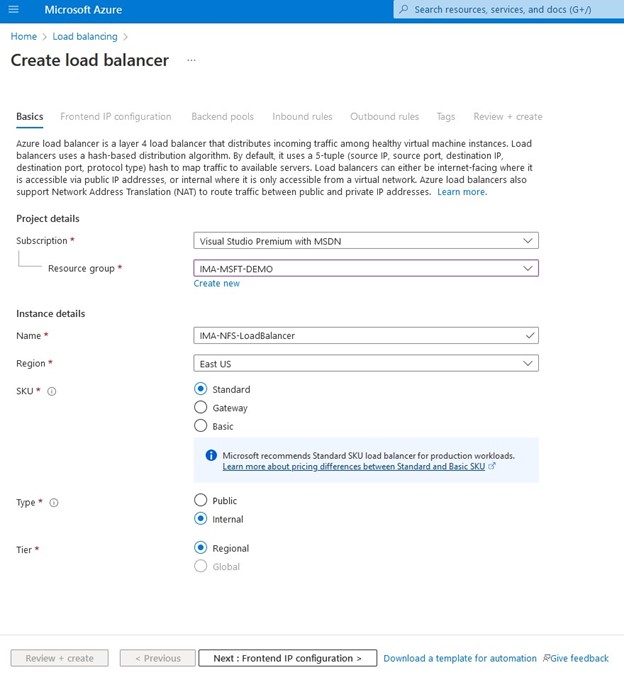
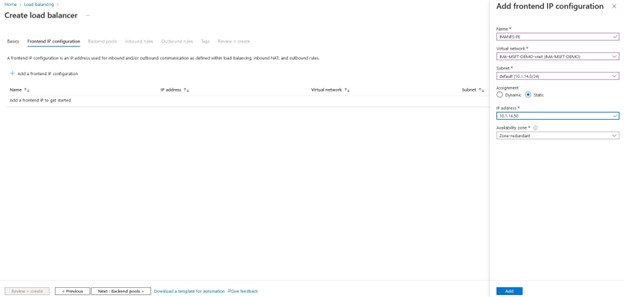
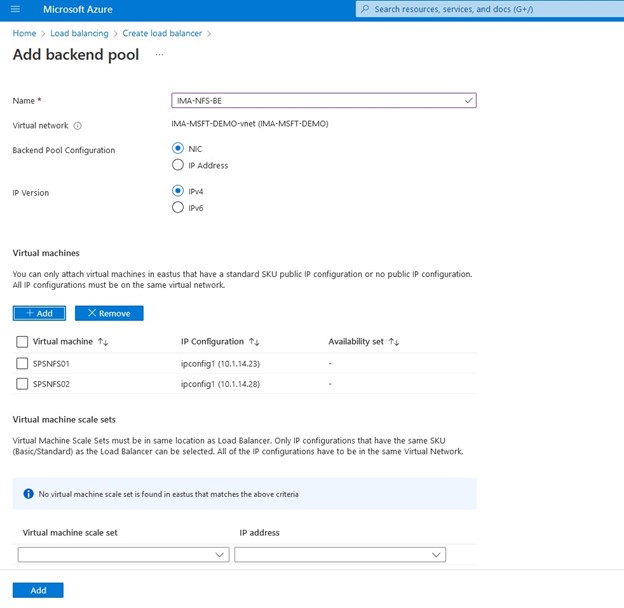
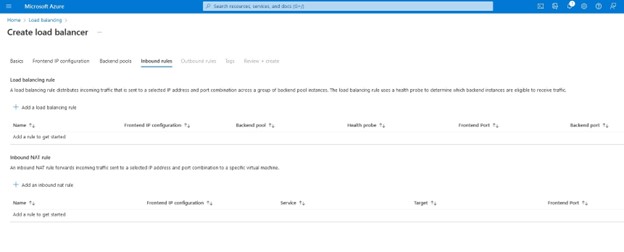
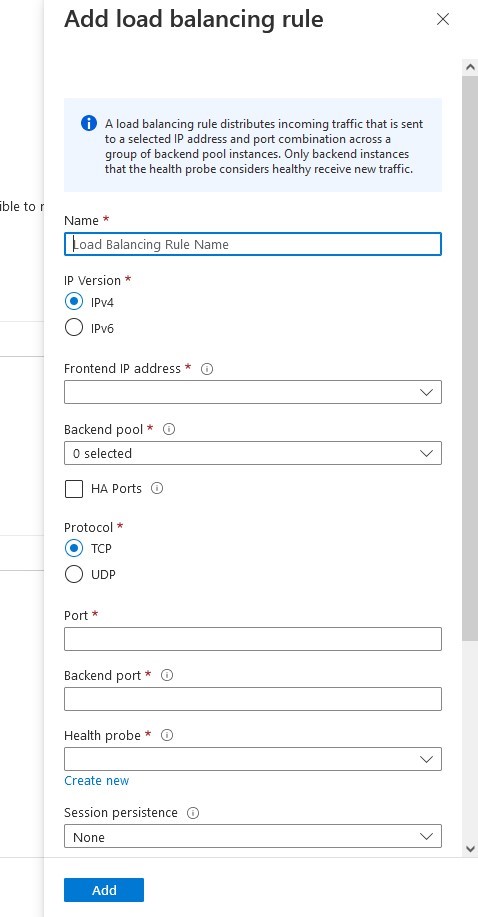
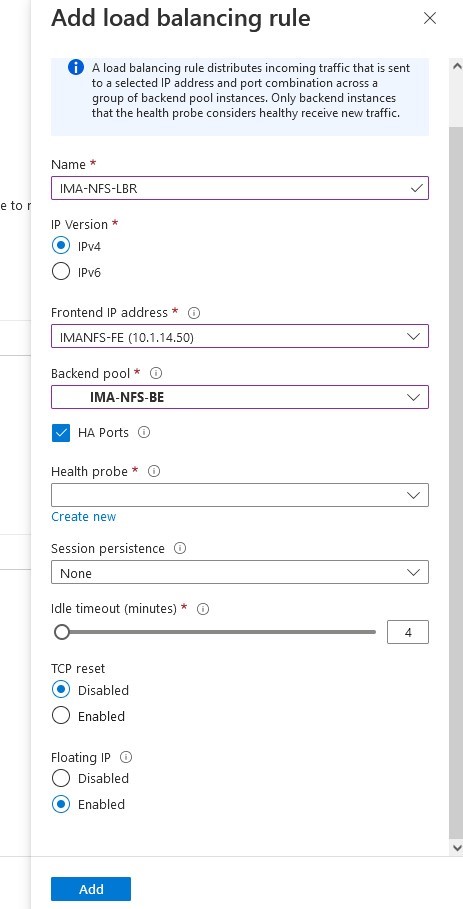
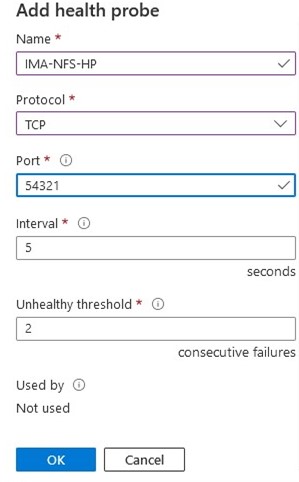
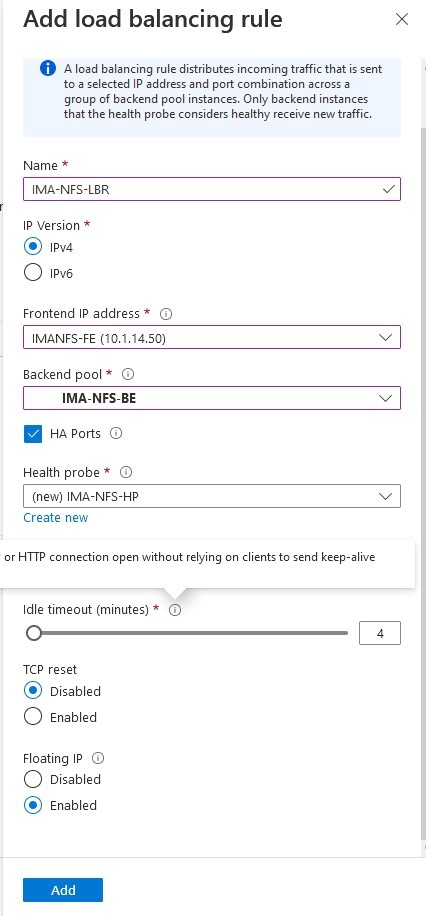
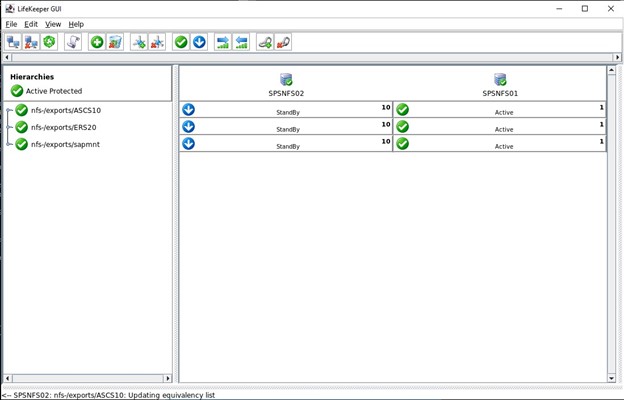
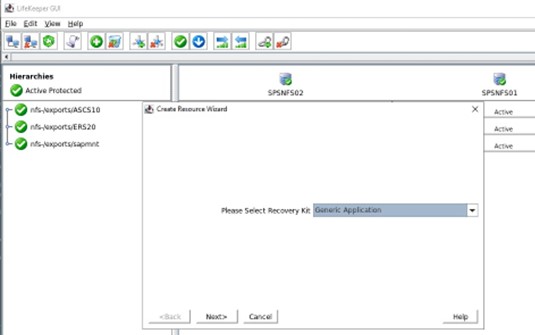
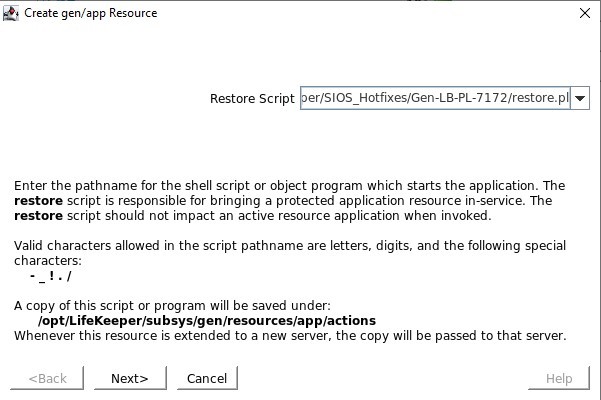
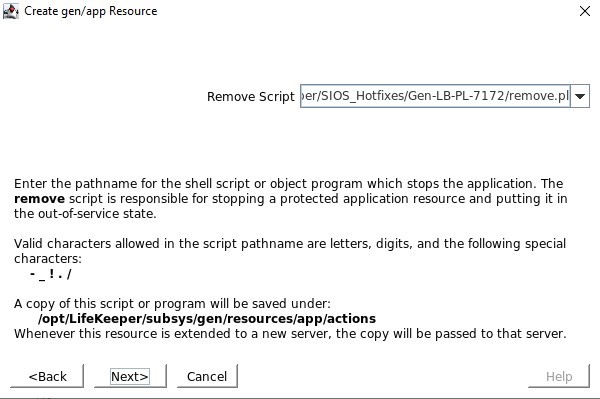
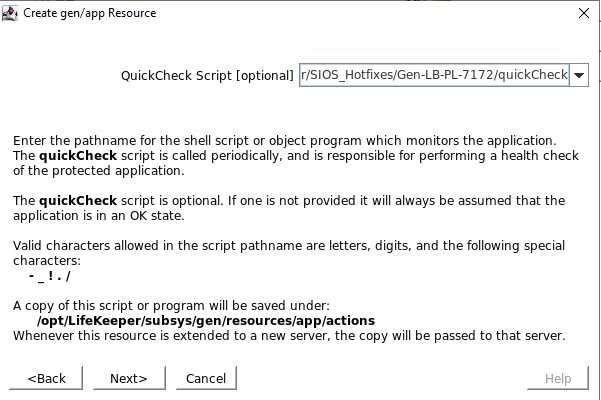
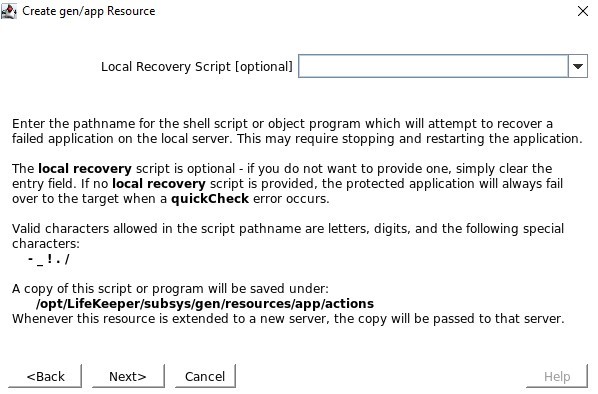
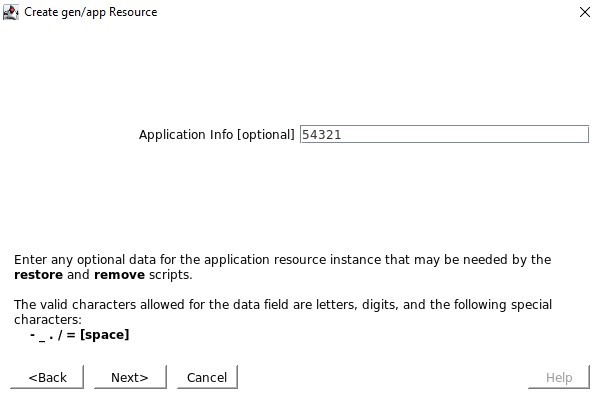
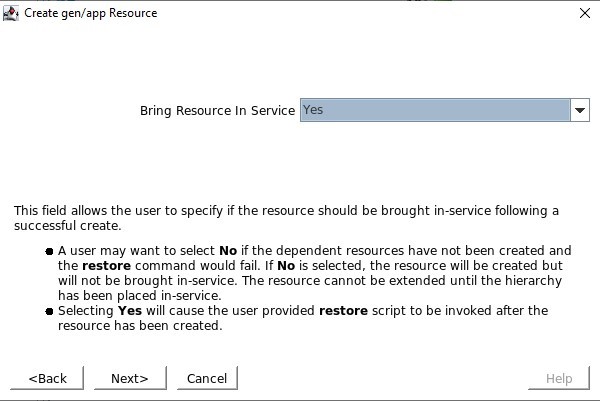
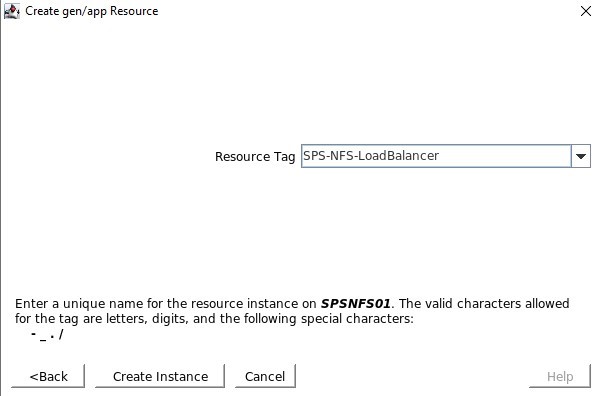
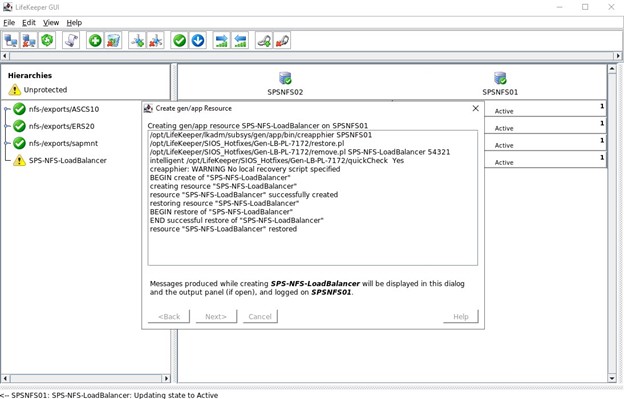
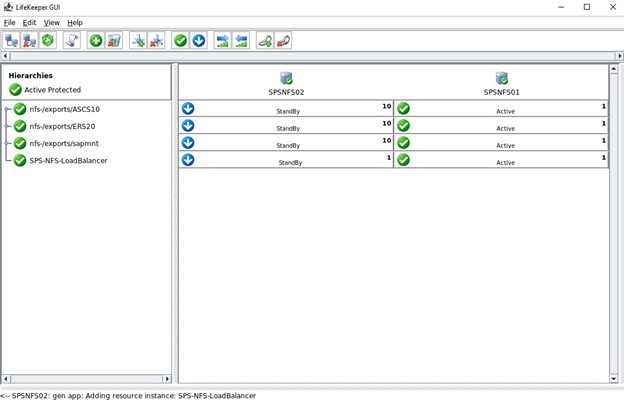
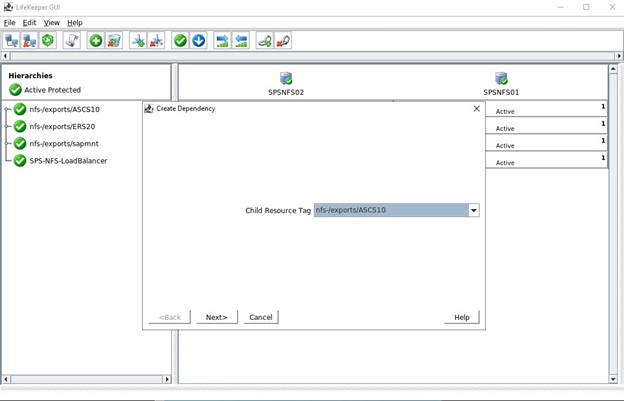
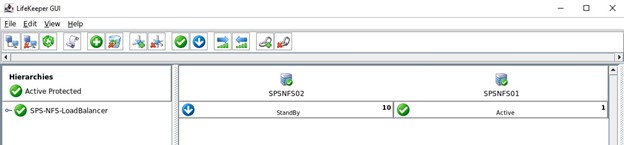
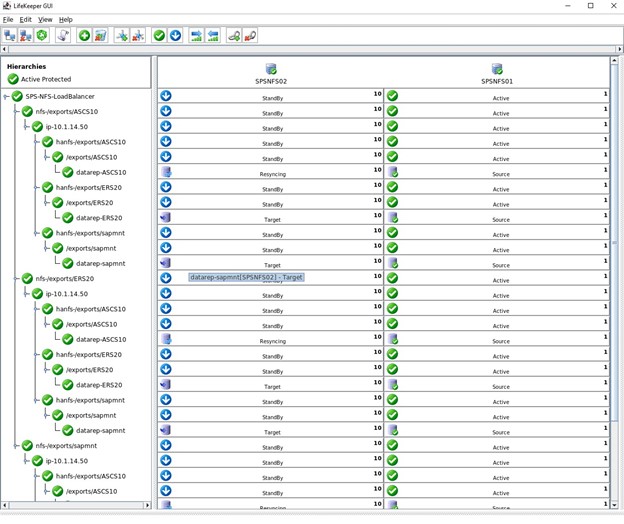

 SIOS SAN and SANless clustering software provides comprehensive SAP certified protection for your applications and data, including high availability, data replication, and disaster recovery in an easy, cost-efficient solution.
SIOS SAN and SANless clustering software provides comprehensive SAP certified protection for your applications and data, including high availability, data replication, and disaster recovery in an easy, cost-efficient solution.