Tips To Maximise Replication Performance For Linux Clustering With Fusion-io
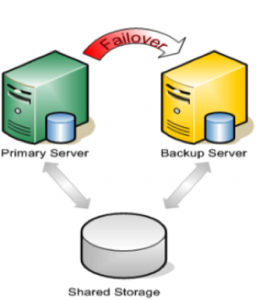
When most people think about setting up a cluster, it usually involves two or more servers, and a SAN – or some other type of shared storage. SAN’s are typically very costly and complex to setup and maintain. Also, they technically represent a potential Single Point of Failure (SPOF) in your cluster architecture. These days, more and more people are turning to companies like Fusion-io, with their lightning fast ioDrives, to accelerate critical applications. These storage devices sit inside the server (i.e. aren’t “shared disks”). Therefore it can’t be used as cluster disks with many traditional clustering solutions. Fortunately, there are ways to Maximise replication performance for Linux Clustering with Fusion-io. Solutions that allow you to form a failover cluster when there is no shared storage involved – i.e. a “shared nothing” cluster.
| Traditional Cluster
|
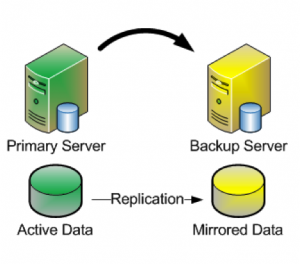
“Shared Nothing” Cluster
|
When leveraging data replication as part of a cluster configuration, it’s critical that you have enough bandwidth so that data can be replicated across the network just as fast as it’s written to disk. The following are tuning tips that will allow you to get the most out of your “shared nothing” cluster configuration, when high-speed storage is involved:
Network
- Use a 10Gbps NIC: Flash-based storage devices from Fusion-io (or other similar products from OCZ, LSI, etc) are capable of writing data at speeds in the HUNDREDS (750 ) of MB/sec or more. A 1Gbps NIC can only push a theoretical maximum of ~125 MB/sec, so anyone taking advantage of an ioDrive’s potential can easily write data much faster than could be pushed through a 1 Gbps network connection. To ensure that you have sufficient bandwidth between servers to facilitate real-time data replication, a 10 Gbps NIC should always be used to carry replication traffic
- Enable Jumbo Frames: Assuming that your Network Cards and Switches support it, enabling jumbo frames can greatly increase your network’s throughput while at the same time reducing CPU cycles. To enable jumbo frames, perform the following configuration (example from a RedHat/CentOS/OEL linux server)
- ifconfig <interface_name> mtu 9000
- Edit /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-<interface_name> file and add “MTU=9000” so that the change persists across reboots
- To verify end-to-end jumbo frame operation, run this command: ping -s 8900 -M do <IP-of-other-server>
- Change the NIC’s transmit queue length:
- /sbin/ifconfig <interface_name> txqueuelen 10000
- Add this to /etc/rc.local to preserve the setting across reboots
TCP/IP Tuning
- Change the NIC’s netdev_max_backlog:
- Set “net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 100000” in /etc/sysctl.conf
- Other TCP/IP tuning that has shown to increase replication performance:
- Note: these are example values and some might need to be adjusted based on your hardware configuration
- Edit /etc/sysctl.conf and add the following parameters:
- net.core.rmem_default = 16777216
- net.core.wmem_default = 16777216
- net.core.rmem_max = 16777216
- net.core.wmem_max = 16777216
- net.ipv4.tcp_rmem = 4096 87380 16777216
- net.ipv4.tcp_wmem = 4096 65536 16777216
- net.ipv4.tcp_timestamps = 0
- net.ipv4.tcp_sack = 0
- net.core.optmem_max = 16777216
- net.ipv4.tcp_congestion_control=htcp
Adjustments
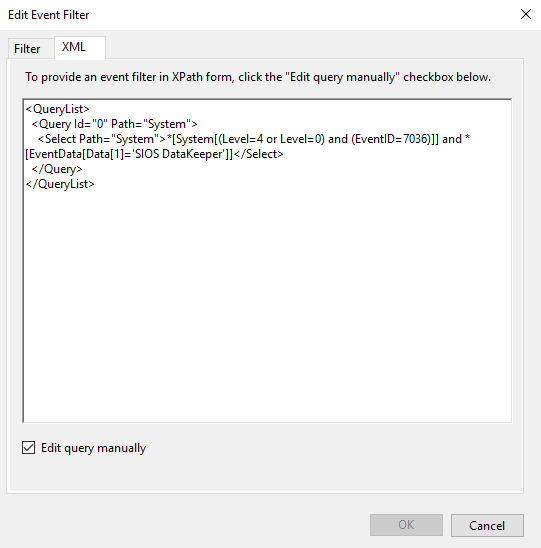
Typically you will also need to make adjustments to your cluster configuration, which will vary based on the clustering and replication technology you decide to implement. In this example, I’m using the SteelEye Protection Suite for Linux (aka SPS, aka LifeKeeper), from SIOS Technologies. It allows users to form failover clusters leveraging just about any back-end storage type: Fiber Channel SAN, iSCSI, NAS, or, most relevant to this article, local disks that need to be synchronized/replicated in real time between cluster nodes. SPS for Linux includes integrated, block level data replication functionality that makes it very easy to setup a cluster when there is no shared storage involved.
Recommendations
In order to Maximise replication performance for Linux Clustering with Fusion-io, let’s try this. SteelEye Protection Suite (SPS) for Linux configuration recommendations:
- Allocate a small (~100 MB) disk partition, located on the Fusion-io drive to place the bitmap file. Create a filesystem on this partition and mount it, for example, at /bitmap:
- # mount | grep /bitmap
- /dev/fioa1 on /bitmap type ext3 (rw)
- Prior to creating your mirror, adjust the following parameters in /etc/default/LifeKeeper
- Insert: LKDR_CHUNK_SIZE=4096
- Default value is 64
- Edit: LKDR_SPEED_LIMIT=1500000
- (Default value is 50000)
- LKDR_SPEED_LIMIT specifies the maximum bandwidth that a resync will ever take — this should be set high enough to allow resyncs to go at the maximum speed possible
- Edit: LKDR_SPEED_LIMIT_MIN=200000
- (Default value is 20000)
- LKDR_SPEED_LIMIT_MIN specifies how fast the resync should be allowed to go when there is other I/O going on at the same time — as a rule of thumb, this should be set to half or less of the drive’s maximum write throughput in order to avoid starving out normal I/O activity when a resync occurs
- Insert: LKDR_CHUNK_SIZE=4096
From here, go ahead and create your mirrors and configure the cluster as you normally would.
Interested to Maximise Replication Performance For Linux Clustering With Fusion-io, see what else SIOS can offer.
Reproduced with permission from LinuxClustering