We Built HANA Multitarget to be a Game-changer
On behalf of the SIOS engineering team that created the new HANA Multitarget feature in SIOS LifeKeeper for Linux v. 9.7.0, we are proud and excited of our accomplishment. It took an experienced team of software developers months of planning before we even started the implementation. We worked through a number of customer use cases, technical requirements, and an impossible list of interdependencies to create a feature that is both unique and powerful.
An Engineer’s Perspective on the HANA Multitarget Feature
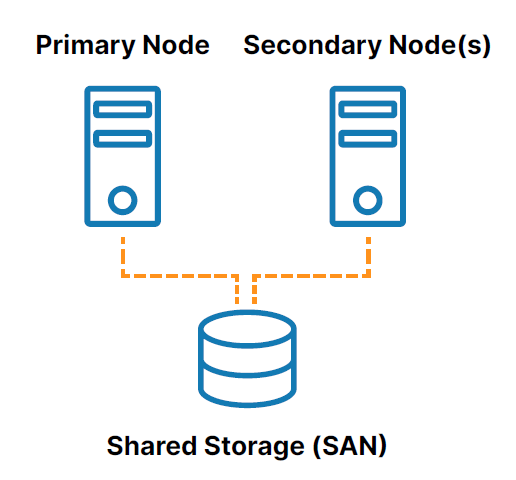
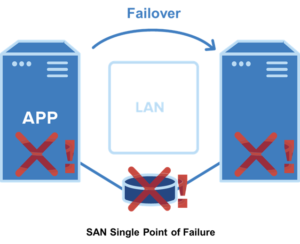
HANA clustering environments are intrinsically complicated. That’s why customers who want to add a third node to their HANA cluster using competing clustering software have to use some pretty complex scripting and continue to script any changes to the cluster in the event of a failover or failback. With these products, after a failover occurs you have to do a lot of manual verification steps to be sure it’s ok to perform a takeover. Unlike those products, LifeKeeper 9.7.0 accesses detailed information about all the HANA nodes in your cluster that make it a much more stable and reliable HA environment. For example, it can determine which nodes are available and capable of a takeover and can also see if there was data loss after the failover occurred. This is very important, especially if multiple nodes have failed.
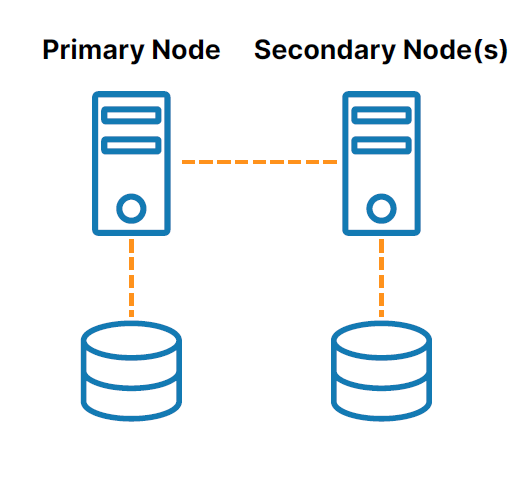
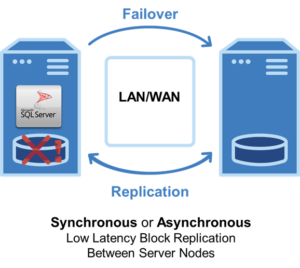
The complexity of managing both failover and replication reliably in a multinode environment increases exponentially with every added node. For example, how will the clustering software choose which node to failover to? With data stored in three nearly identical locations, which storage is most current and accurate? How do you guard against a “split brain” scenario where data on different nodes diverge? What should the failover and replication steps be if two nodes fail? Three? We faced the challenge of thinking through the various combinations of failure scenarios and ensuring that SIOS maintained data protection and a reliably failover in each of them.
LifeKeeper monitors the environment at a deeper level than competing products and has stringent requirements for managing failovers. The new 9.7.0 version of LifeKeeper has an enhanced ability to keep track of the HSR hierarchy, and to manage failovers of complex three and four-node HSR clusters to ensure they are fast and highly reliable.
We set out to create the most automated and reliable multitarget clustering environment for HANA in the industry and I believe we succeeded.
Why HANA Multitaget Provides the Most Reliable Clustering Environment
- We put just as much time into rigorous testing as we put into development to make sure the systems would be as predictable and stable as possible.
We eliminated an amazing amount of manual steps. There is no comparison to other clustering software. SIOS LifeKeeper is by far the most automated and reliable solution for multitarget clustering. - Extensive effort went into research and development. The team worked on multiple design options before settling on the final implementation.
- After we developed and tested the third-node functionality, we continued our development efforts to support a fourth DR node to give our customers disaster recovery with even more reliability and stability.
- The entire team really took testing as seriously as possible, and continuously tested the HANA failover and recovery processes themselves during development.
- Our documentation team also worked hard to create detailed, easy-to-use documentation about the implementation, operation, and management of a HANA multitarget system controlled by LifeKeeper.
We believe the new LifeKeeper HANA Multitarget is a game-changer that gives customers the most automated, reliable failover clustering solution in the industry. Watch a demo of the new feature to see its capabilities.
Contact SIOS today for more information on the HANA Multitarget feature for LifeKeeper.
Reproduced with permission from SIOS